
We empower accounting teams to work more efficiently, accurately, and collaboratively, enabling them to add greater value to their organizations’ accounting processes. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. As you work through this part, remember that fixed assets are considered non-current assets, and long-term debt is a non-current liability. High-debt companies may retain more earnings to reduce debt and improve financial health.
Retained Earnings inside the Balance Sheet
- A net profit would lead to an increase in retained earnings, whereas a net loss would reduce the retained earnings.
- Retained earnings, at their core, are the portion of a company’s net income that remains after all dividends and distributions to shareholders are paid out.
- This number’s a must.Ultimately, before you start to grow by hiring more people or launching a new product, you need a firm grasp on how much money you can actually commit.
- To help you better understand these bookkeeping basics, we’ll cover in-depth explanations of debits and credits and help you learn how to use both.
- This increase in retained earnings is credited to Retained Earnings Account.
A maturing company may not have many options or high-return projects for which to use the surplus cash, and it may prefer handing out dividends. To simplify your retained earnings calculation, retained earning debit or credit opt for user-friendly accounting software with comprehensive reporting capabilities. There are plenty of options out there, including QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks.
- Accordingly, companies with high retained earnings are in a strong position to offer increased dividend payments to shareholders and buy new assets.
- Paid-in capital is the actual investment by the stockholders; retained earnings is the investment by the stockholders through earnings not yet withdrawn.
- Now, you must remember that stock dividends do not result in the outflow of cash.
- A journal is a record of each accounting transaction listed in chronological order.
Debit vs. credit accounting FAQ
To see how retained earnings impact shareholders’ equity, let’s look at an example. This line item reports the net value of the company—how much your company is worth if you decide to liquidate all your assets. The retained earnings are recorded under the shareholder’s equity section on the balance as on a specific date. Thus, retained earnings appearing on the balance sheet are the profits of the business that remain after distributing dividends since its inception. Since stock dividends are dividends given in the form of shares in place of cash, these lead to an increased number of shares outstanding for the company. That is, each shareholder now holds an additional number of shares of the company.
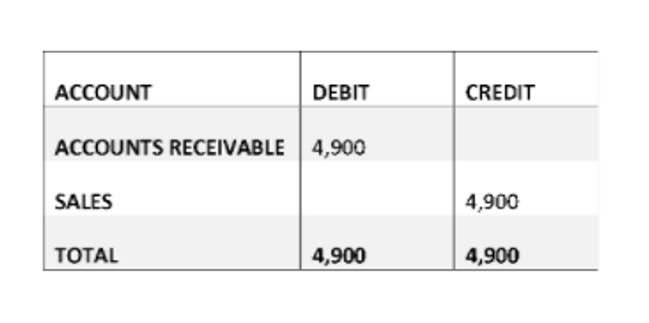
Accounting journal entry example
Liabilities are on the right side of the accounting equation.Liability account balances should be on the right side of the accounts. Assets are on the left side of the accounting equation.Asset account balances should be on the left side of the accounts. We will use the accounting equation to explain why we sometimes debit an account and at other times we credit an account. The statement of changes in retained earnings sample shown below is typical of how a business will present the balance of retained earnings. The dividends are the amount which has been declared for the year not the amount paid during the year. Well-managed businesses can consistently generate operating income, and the balance is reported below gross profit.

The statement of retained earnings is one of four main financial statements, along with the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. In that case, the company may choose not to issue it as a separate form, but simply add it to the balance sheet. It’s also sometimes called the statement of shareholders’ equity or the statement of owner’s equity, depending on the business structure. Net Profit or Net Loss in the retained earnings formula is the net profit or loss of the current accounting period. For instance, in the case of the yearly income statement and balance sheet, the net profit as calculated for the current accounting period would increase the balance of retained earnings.
The purpose of a balance sheet is to ensure all your bookkeeping journal entries are correct and every penny is accounted for. Alternately, dividends are cash or stock payments that a company makes to its shareholders out of profits or reserves, typically on a quarterly or annual basis. Retained earnings allow businesses to fund expensive asset purchases, add a product line, or buy a competitor. Your firm’s strategy should influence how you choose to use retained earnings and cash dividend payments.

If the balance in the Retained Earnings account has a debit balance, this negative amount of retained earnings may be described as deficit or accumulated deficit. Fortunately, accounting software requires each journal entry to post an equal dollar amount of debits and credits. If the totals don’t balance, you’ll get an error message alerting you to correct the journal entry. Implementing accounting software can help ensure that each journal entry you post keeps the formula and total debits and credits in balance. Retained earnings represent the total profit to date minus any dividends paid.Revenue is the income that goes into your business from selling goods or services.

What is the Normal Balance in the Retained Earnings Account?
Thus, the balance in Retained Earnings represents the corporation’s accumulated net income not distributed to stockholders. A statement of retained earnings shows the changes in a business’ equity accounts over time. Equity is a measure of your business’s worth, after adding up assets and taking away liabilities. Knowing https://www.bookstime.com/articles/what-is-accountancy how that value has changed helps shareholders understand the value of their investment. One piece of financial data that can be gleaned from the statement of retained earnings is the retention ratio. The retention ratio (or plowback ratio) is the proportion of earnings kept back in the business as retained earnings.
- The statement of retained earnings (retained earnings statement) is a financial statement that outlines the changes in retained earnings for a company over a specified period.
- The amount retained still belongs to the equity holders and forms part of the owners equity.
- The specific use of retained earnings depends on the company’s financial goals.
- Over the same duration, its stock price rose by $84 ($112 – $28) per share.
- Instead, they reallocate a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts.
- Retained earnings are a type of equity and are therefore reported in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- The schedule uses a corkscrew-type calculation, where the current period opening balance is equal to the prior period closing balance.
- Retained earnings are calculated through taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding to the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts.
- In financial modeling, it’s necessary to have a separate schedule for modeling retained earnings.
- Since stock dividends are dividends given in the form of shares in place of cash, these lead to an increased number of shares outstanding for the company.
- The goal is to maintain a balance that supports your business’s health and strategic goals while meeting shareholder expectations.
- Yes, retained earnings carry over to the next year if they have not been used up by the company from paying down debt or investing back in the company.
- Additional paid-in capital reflects the amount of equity capital that is generated by the sale of shares of stock on the primary market that exceeds its par value.
As you process more accounting transactions, you’ll become more familiar with this process. Take a look at this comprehensive chart of accounts that explains how other transactions affect debits and credits. The data in the general ledger is reviewed, adjusted, and used to create the financial statements. Review activity in the accounts that will be impacted by the transaction, and you can usually determine which accounts should be debited and credited. A company’s general ledger is a record of every transaction posted to the accounting records throughout its lifetime, including all journal entries.

